I love doing media work and this was especially fun as the radio crew came to me! We broadcast my part live from my lounge. Have a listen:
So normally I am not pro diets. However there is always an exception and this is it. The Mediterranean diet is the way I try to eat and drink. I prefer to call it an eating plan or a lifestyle rather than a diet. It is one of those diets that is good for your overall health and could have a great protective and preventative effect on chronic disease such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
There is some really good research on this way of eating. Large scale randomised trials conducted over a number of years with deent follow up. This is what we like. So the evidence shows that the Mediterranean diet definiately has good implicaitons for heart disease and type 2 diabetes. For overall health it is a very good way to be eating.
The PREDIMED study followed 7447 people aged 55-80yrs who were at high risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD), for 5 years. They were randomised to:
- Mediterranean diet with 1 litre of olive oil a week
- Mediterranean diet with 30g/d nuts
- Low fat control group
The data has been analysed in a number of different studies. Here is my short summary.
Cardiovascular Disease:
Estruch et al (2013) found the Mediterranean groups had a
- 30% reduction in the risk of death from CVD
- 39% reduction in stroke
- These results were only significant in men and less than expected but still show the benefits of the Med diet for heart diease.
Metabolic Syndrome:
Salas-Salvado et al (2008) looked at the data from 1224 people after 1 year of the diet. 61.4% of people at the start had Metabolic syndrome (abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, raised blood sugar levels and blood lipid levels) and found:
- 6.7% reduction in metabolic syndrome in the olive oil group
- 13.7% reduction in the nuts group, which was statiscally significant. So a Med diet with nuts may have reveress metabolic syndrome.
Cholesterol:
Monteserrat et al (2007) looked at 372 of the subjects at the 3 month marker and found the levels of LDL cholesterol reduced in the Mediterranean diet groups. The high levels of antioxidants in the diet was concluded to the be cause of this. Olive oil, nuts, fruit, vegetables and legume intake was all increased in the Meditteranean diet groups and all these foods contain antioxidants.
Blood Sugars:
Blood sugars were looked at in 772 people at 3 months bu Estruch et al (2006). They found in the Med groups:
- Blood sugars reduced
- Systolic blood pressure reduced
- Total:HDL cholesterol reduced
- C reactive protein reduced (a marker of inflammation).
Looking at type 2 diabetes, Salas-Salvado (2011) found the risk was overall reduced by 52% in those on the Med diets. Only 10-11% of people on the Mediterrrean diets developed type 2 diabetes compared to 17.9% in the control group.
Lyon Heart Study:
The Lyon Heart Study is another good quality piece of research. 605 middle aged subjects who had already had a heart attack were followed for 4 years and were randomised to either:
- Mediterranean diet with an omega-3 rich margarine
- Western style diet
The results showed:
- 72% reduction in death from heart disease
- a reduced rate of recurrance of heart attacks
Weight Loss:
- Esposito et al (2008) followed 180 patients with metabolic syndrome for 2.5 yrs. They were put on the Mediterranean diet or a low fat diet. At the end the Mediterranean group had lost more weight at 4.0kg compared to just 1.2kg in the low fat group. The Mediterranean diet group also had reduced the occurance of metabolic syndrome with only 44% of people still having it.
- Shai et al (2008) looked at 322 obese people, putting them on a:
- Low fat calorie controlled diet – weight loss of 2.9kg
- Mediterranean calorie controlled diet – weight loss of 4.4kg
- low carbohydrate diet that was not calorie controlled – weight loss of 4.7kg
So a Mediterranean diet may help with weight loss too. Here is a post on the Mediterranean diet explaining what it is and what foods to eat more of.
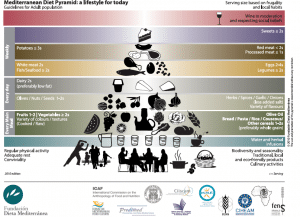
Other Sources:
Authority Nutrition: 5 studies on the Meditteranean Diet: Does it really work?
PENNutrition

The best diet is still the discipline on eating.
I been researching a good diet that will work for me, I tried to look at fruit diet and trying to incorporate in my diet the rainbow fruit diet which is composed of fruits and bolder color the fruit is the better. The other diet that I am about to try is the Paleo diet which is the diet of our caveman ancestors, and now by reading this post, I would like to try next in line the Mediterranean diet. Thank you for this insightful post about Mediterranean diet and I will surely try this in the upcoming future.